9 Steps To Improve Your Medical Website Content
Start With Keyword Research
Writing medical content that has strong SEO attributes means your content will focus on providing users with valuable information that answers their queries. Additionally, it means optimising for keywords and key phrases that help search engines understand your content.
By writing well-optimised content for your patients and search engines will improve your page or posts search relevancy and push you closer to the top of search engine results pages (SERPS).
By building an SEO strategy into your writing, you can aim to increase traffic to your site and grow your audience.
Over time (or even rather quickly), it can be cheaper, more consistent, and sometimes more effective than paid advertising.
How to Pick a Primary Keyword
When you’re writing with SEO in mind, it’s tempting to take as many keywords as possible and optimise the text for all of them. However, this may lead to convoluted, disorganised content.
So, pick one primary keyword and then dig deeper. Your primary keyword should be the main focus of the entire article.
Choosing high-volume keywords are popular, but they are also challenging to start ranking for in the short term.
Keyword difficulty can vary. Some may have high volumes with lower difficulty, while others may have lower volumes and higher difficulty scores. It depends on your niche!
Medicine can be quite competitive so it is best to target keyword phrases with low difficulty and high volume.
How to Pick Additional Keywords for SEO Writing
Additional keywords should be closely related to your primary keyword so that inserting them doesn’t change the article’s focus but instead supports the main keyword.
You can pick them from the topic clusters to the left, or 'Related' and 'Questions' tabs on top in the Keyword Magic tool.
Now that you’ve looked through and identified keywords you’re going to target, let’s dive into the next step: researching what is performing.
9 Steps to Create Great SEO Content
✍ Strong SEO Writing Needs Good Keyword Research
✍Create a Well-Optimized Meta Title
✍Create a Catchy H1
✍ Add Visual Content
✍ Make Your URL Readable
✍ Determine Search Intent and Identify the Right Format
✍ Optimize the Meta Description
✍ Content Structure and Readability
✍ Adjust Interlinking
Research Your Topic
In SEO, writing great content is the key. To write great content, you need to know two things:
- Know who your audience is, and
- Know what topics matter to them by answering questions they have and provide them with solutions.
Determine Search Intent and Identify the Right Format
Search intent can be defined as what a user is searching for. Google devotes a lot of attention to teaching algorithms to evaluate user intent correctly and encourages content creators to answer the requests with relevant material.
The content format you choose, the message you convey, and the call-to-action you leave should depend on the search intent for a keyword. Search intent can be broken down into four distinct types:
- Informational — the searcher is looking for specific information on a topic.
- Navigational — the searcher is looking for a specific web page or site.
- Commercial — the searcher is considering a purchase and wants to investigate their options.
- Transactional — the searcher wants to purchase something.
Here are some standard terms that are used with these different types of keywords:
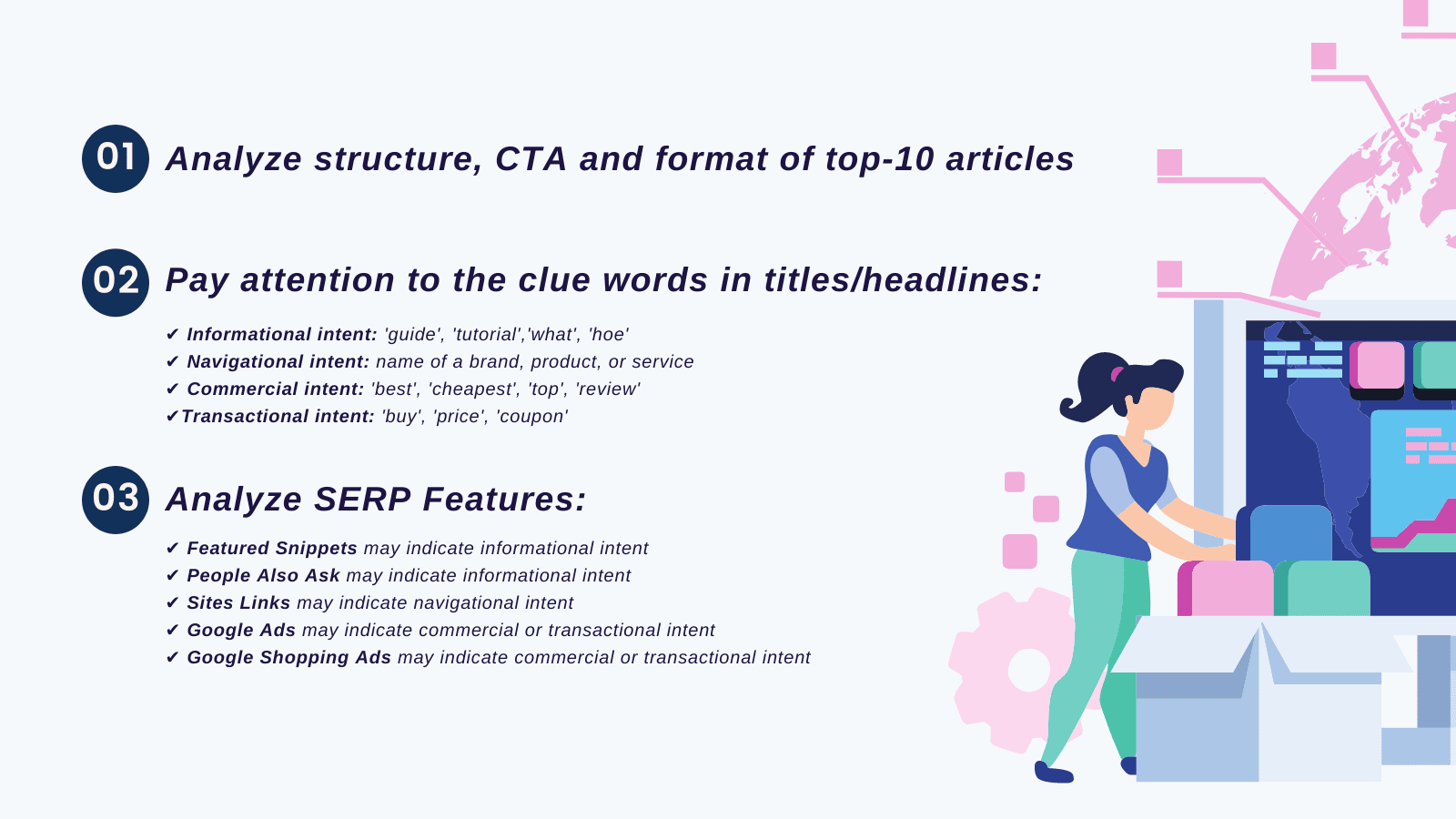
- Informational: ‘guide,’ ‘tutorial,’ question words, such as ‘what,’ ‘how,’ or lists with ‘top,’ ‘best,’ ‘checklist’ in the title (e.g. ‘best music festivals 2021’).
- Navigational: the name of a brand, product, or service (e.g., ‘ultra music festival’).
- Commercial: product modifiers like ‘cheapest,’ ‘review,’ ‘comparison’ (e.g., ‘ultra music festival reviews’).
Transactional: ‘buy,’ ‘price,’ ‘coupon,’ etc. (e.g., ‘ultra music festival tickets’). The clue words will help you determine the type of search intent.
You may also want to type your keyword into the Google search bar to check for any SERP features that can help with identifying the keyword type:
- Featured snippets may indicate informational intent
- People Also Ask may also indicate informational intent
- Site links may indicate navigational intent
- Google Ads may indicate commercial or transactional intent
- Google Shopping ads may indicate commercial or transactional intent
Considering the search intent and keyword type, you can now identify the best format for your article.
This is where manual search can help you — look at competitors’ pages that are already ranking in the top 10 for your keywords. Are they step-by-step guides, or maybe a list of different options? What do the articles call for? What are their titles, i.e., how do they describe their piece for search results?
Also, you can use Topic Research to quickly find out what people on the internet ask about the topic.
The Mind Map within the tool presents a ready list of potential topics to cover. You can choose any of them to see the exact questions people ask:
3. Create a Well-Optimised Meta Title
Your article’s headline is not necessarily the title shown in search results. Consider that your article has two headings: the H1 tag displayed on the page and the meta title tag shown in the search results snippet.
They can be closely related or similar, but they don’t necessarily have to be identical. The most important thing when writing for SEO is that each tag must contain your target keyword.
Although the H1 tag is one of the signals showing search engines how the page is structured, the meta title is more important for SEO purposes.
The meta title introduces your content to the audience. That's why it's often the primary piece of information a user uses to decide which result to tap on, especially when searching on mobile.
To make your title attractive for both search engines and searchers, follow the basic rules:
- Write a unique title for each page. If you use the same title on different web pages, Google can show an alternative title instead of yours.
- Consider the user intent. Choose a title that indicates what problem users will solve or the benefit they will get from reading your content. Include the clue words to catch users’ attention and entice them to click.
- Keep the title between 15 to 40 characters long. The maximum length is approximately 60 characters - any text beyond that can be truncated automatically.
- Include your target keyword in titles. Search engines use titles to understand whether the content is relevant to the query. However, don't over-optimize.
4. Create a Catchy H1
If you need to add more creativity to your article, there’s a little more room in the H1 tag than in the title tag. Here’s what you need to consider when writing your H1 heading:
- Create a unique H1. This will help prevent visitors from getting lost between similar pages on your site.
- Use words like 'how', 'why', 'what', and 'where'. This way, you help people understand what they will find on the page below — guides and how-to articles also drive 2x more traffic than other types.
- Use numbers like 'top 10', '5 best', 'N things…', etc. Articles with list headlines get 2x more traffic and 2x more social shares than other types.
- Describe what is discussed in the text body. The H1 of the page should describe the content; otherwise, Google regards the discrepancy as low content quality.
Topic Research can help you quickly find the most resonating headlines. After entering a topic, you’ll instantly see popular headlines that have the highest amount of backlinks and social engagement.
5. Optimise the Meta Description
The meta description is what users see under the page title in Google results. It can be the perfect way to encourage a user to click on your link over your competitors’ if you write it carefully.
To properly optimise the meta description, there are five basic recommendations:
- Make sure that every page on your site has a meta description. Also, create meta descriptions that accurately describe the specific page.
- Include a relevant keyword in the meta description.
- Keep them about 1-2 sentences (140-160 characters) long. Even though there’s no limit on how long a meta description can be, search result snippets are typically truncated to fit the device width.
- Meta descriptions don't just have to be in sentence format; it’s also a great place to include the critical information scattered throughout a page. For example, product pages might have a price, age, manufacturer in their description. These descriptions become even more attractive for both search engines and users.
- Target an emotion and add a call-to-action if it’s relevant.
The meta description is one of the best ways to grab the attention of new visitors, so give this optimization step enough attention.
6. Content Structure and Readability
Imagine you open one of the results in the SERP, and there’s one continuous piece of text. How likely would you be to continue reading? You’ll probably try to use the Ctrl+F shortcut or just leave to find a better-structured article.
Good structure is an essential element of high-quality content development. Subheadings make your content scannable and easier to read. According to our study, 36% of articles with H2 and H3 tags have higher performance in terms of traffic, shares, and backlinks.
Here are some recommendations on how to make your content readable:
- Make your text long if it’s necessary. Long reads of 3000+ words get 3x more traffic, 4x more shares, and 3.5x more backlinks than articles of average length (901-1200 words). But this doesn’t mean that a short article is bound to rank poorly — it depends on what users need.
- Consider adding a table of contents. If the article is long, add a table of contents at the beginning of the article to let visitors quickly go to the desired section.
- Use H2 and H3s. Well-structured articles with both H2 and H3 tags are more likely to be high-performing. Structure the article to make it easier for the user to understand the content, but don’t overdo it by making the structure too complex with multiple subheadings.
- One paragraph equals one idea. Divide the content into logical, digestible segments to keep readers engaged.
- Answer user questions. Attract users' attention by including their questions in subheadings.
- Highlight important ideas. You can use bold font or change the font size. This helps to emphasise, makes the text easier to follow, and helps cement the main ideas in users’ minds.
- Divide long sentences. Just like breaking your content up into paragraphs, divide long sentences into shorter ones.
- Use bullets and numbered lists. Using them, you can convey large amounts of information in a concise form. Bullet points also increase your chances of getting a Featured Snippet.
Add Visual Content
Besides optimising your writing for SEO, images are an essential piece of the content puzzle.
Different visuals across a page can help convey information to the user better and circulate your content better.
Use infographics, checklists, templates, and other types of visual content to deliver value to your audience faster and in a more catchy way.
The more valuable, engaging, and relevant content is, the more backlinks you are likely to get. Backlinks from authoritative websites make your content trustworthy for Google. Thus, the search engine ranks it higher.
The other benefit of pictures and videos to any blog post or copy is that they can be ranked in the Images and Video sections of Google and even get into Featured Snippets and attract additional traffic.
Be sure to optimise your visual content. Below, you’ll find the main things you should do.
Reduce the image size.
Images are often the most significant contributor to overall page size and can make pages slow and expensive to load. If you resize images to their maximum display dimensions, you'll almost always find that your site loads faster, bringing improved SEO benefits and a better user experience.
PRO TIP: analyse your site speed with PageSpeed Insights.
Create descriptive image names.
Using 'music-festival-people.jpg’ is a much clearer way to tell what an image shows than ‘IMG00353.JPG.' Change a generic filename to a descriptive name to give Google clues about the subject matter of the image.
Add alt tags.
Alt tags provide a text alternative to an image for search engines and those using screen readers to access a web page.
There are a few best practices when adding image alt texts:
- Describe the contents of an image in as much detail as possible. This will help it rank on Google Image Search and give context about how it relates to your page's content.
- Make alt tags relevant to the topic of the page that it is on.
- Be sure to write unique alt texts that describe the specific contents of the image rather than repeating the page's main target keyword or other images’ alt tags.
Find more tips to help you optimise images in our guide.
Make Your URL Readable
It’s essential to write a quality URL that clearly describes the page's content to help your readers understand what the page will be about.
URLs get copied and pasted regularly, and sometimes when a link has no anchor text, the URL itself serves as the anchor text. In other cases, users can hover on the text to see the link in the lower-left corner of the browser window. A readable URL explains what is inside.
Which of the links would you trust more: ‘https://www.example.com/endometriosis-diagnosis/’ or ‘http://www.example.com/index.php?id_sezione=360&sid=3a5ebc944f41daa6f849f730f1’?
A site's URL structure should be as simple as possible. Remember that based on only these few words, users’ brains decide whether this content is helpful for them or not.
Here is what Google recommends to keep a URL readable:
- Use punctuation in your URLs, and use hyphens (-) instead of underscores (_) between words.
- Make your URL descriptive and match the page's primary keyword.
- Use lowercase rather than mixing in capital letters.
- Make it as short as possible while still describing the contents of the page.
Adjust Interlinking
Internal links are links that point from one page to another on your website. Having a solid internal linking structure ensures that you point users and search engines to valuable, relevant pages with other content to reference.
According to Google: "Some pages are known because Google has already crawled them before. Other pages are discovered when Google follows a link from a known page to a new page.”
- Internal linking helps search engines.
To add your site pages to its massive database of discovered URLs, Google sends robots to investigate your site. Robots fetch a few web pages and then follow the links to find new URLs. So, for search engines, interlinking is used to discover contextually relevant content on your site.
Besides showing your site's structure and offering relevant content, internal links pass authority between pages and ultimately may improve rankings. If a page, for instance, has authoritative external links pointing to it, it will have built up a PageRank score. This authority can then be passed to another page of your site by way of internal links.
- Internal linking helps people.
For users, interlinking is also a significant element in helping to navigate and find more helpful information on your website.
Internal linking should not be done once, but something that needs to be monitored constantly. Here are our suggestions on how to create internal linking.
Conduct an audit.
An audit of existing content will help you understand which topics your content covers and which ones it doesn’t, which articles are relevant and worth referring to, and which ones are worth updating, etc.
The Semrush Site Audit Tool has a Thematic Report checking your site’s internal linking, showing:
- How reachable your articles are — how many clicks are required to get them from the main page.
- The pages that have a weak Internal LinkRank and those passing most Internal LinkRank — this can help you identify the less and more authoritative pages on your site.
- Internal link issues — errors, warnings, or notices relating to internal links.
Optimise internal linking.
Find relevant content on the site and add links pointing to new articles. This can help to improve your website architecture and decrease your bounce rate.
You can also optimise your internal linking according to the buyer’s journey to make them move to the next stage. Awareness content should link to Consideration articles, and Consideration articles should link to Decision content, not the other way around.
To make readers interested in other content and make moving through the funnel easier, add related articles at the end of each post.
3. Build your internal linking strategy.
Make a list of the content hub pages to help you build out topic clusters to better understand your site architecture. These pages often drive the most valuable traffic to your site and typically target your main keywords with the best content.
Create topic clusters using internal links. This means that you associate the main hub page for a particular topic with a group of supporting pages to add depth to the topic. You can create a spreadsheet for each topic cluster first and then add links.
Create the right anchor texts. Make them relevant to the article you’re linking to, place them naturally, and consider using the longer-tail variants of your keywords. They could help to boost the rankings for that specific term for your target page, so long as it’s written in a way in which people genuinely search.